Why Quantitative Cell Imaging Over MTT Assay?

Live Cell Imaging
- Label-free
- Direct cell count
- No preparation needed
- Real-time assay
- Single-cell resolution
- Quantitative
MTT assay
- Cytotoxic
- Indirect metabolism activity
- Reagent preparation needed
- Endpoint assay
- Only population-level data
- Qualitative
Meet HoloMonitor®
Our Live Cell Imaging Microscope
- Label-free and high automation
- More biological relevant and less labor-intensive
- Real-time monitoring directly from the incubator
- Robust system with standard cell culture vessels
Use your cells for more than proliferation
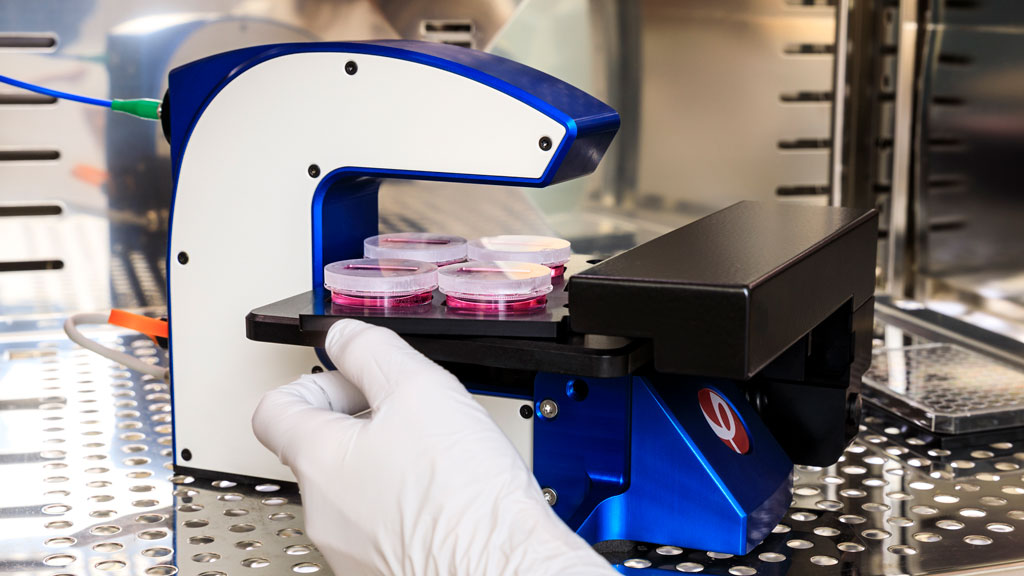
HoloMonitor’s cell-friendly nature makes it an ideal tool for viewing and analyzing live cell cultures. All HoloMonitor live cell assays are label-free, reducing the risk of unwanted toxicity and allowing cell samples to be reused. Hence, HoloMonitor saves your time and money. But foremost, save hard-to-get cells.

The HoloMonitor M4 is a beneficial device for live-cell imaging, providing a lot of data. The good thing is that you can analyze your experiment using one software assay, and later, you can rerun the recorded data in another assay, which allows you to get the maximum from your experiment. I like it and would recommend it to all people doing a cytotoxicity assessment based on cell proliferation and optical thickness of the adherent unstained cells.
Sasa Vasilijic, PhD
Stanford University
Get multiple results from just one sample
Achieve better cell proliferation data
Unlike the MTT assay, which only gives end-point data, HoloMonitor measures kinetic cellular characteristics at multiple time points in real-time. Hence, you can simultaneously compare the temporal effects of multiple treatments and/or conditions. Moreover, you can re-analyze your results with other HoloMonitor assays to generate more data without setting up new experiments.
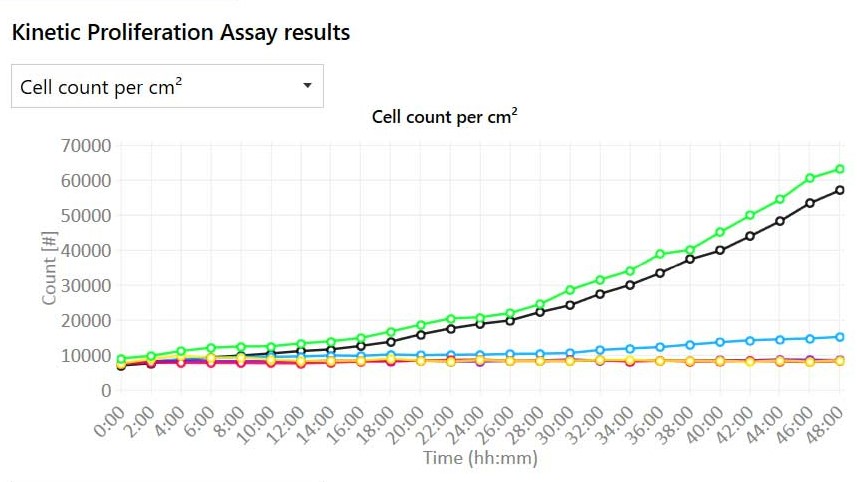
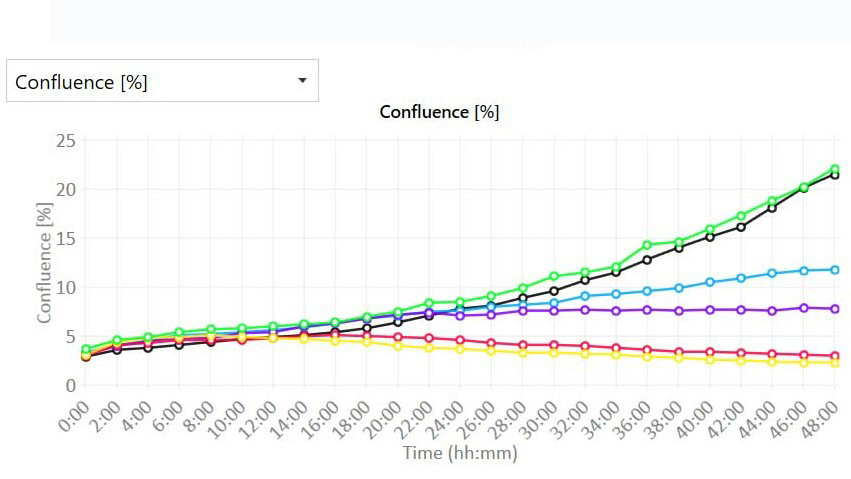
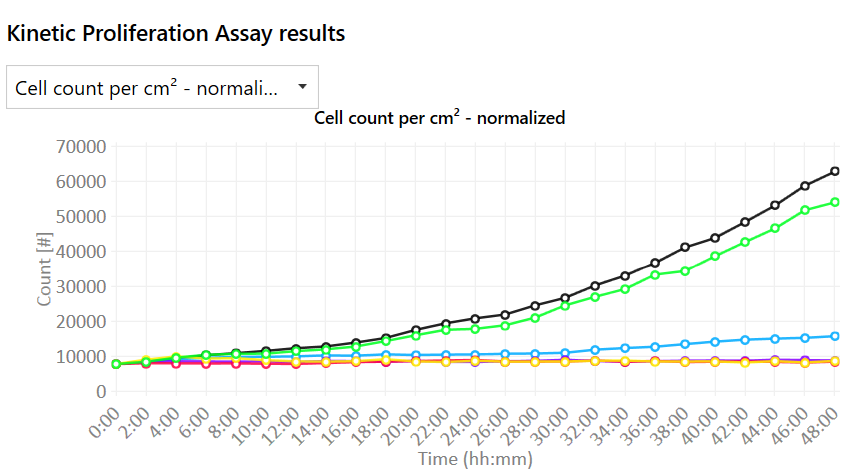
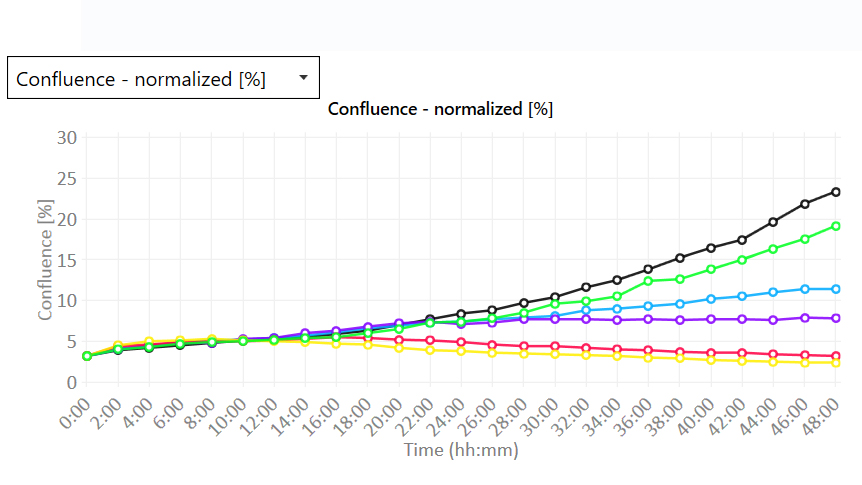
Proliferation data with quantitative imaging
- Real-time growth curves with or without normalization:
- Cell count (cells/cm2)
- Confluence (%)
- Multiwell cell images and time-lapse videos
Get accurate data with digital holography
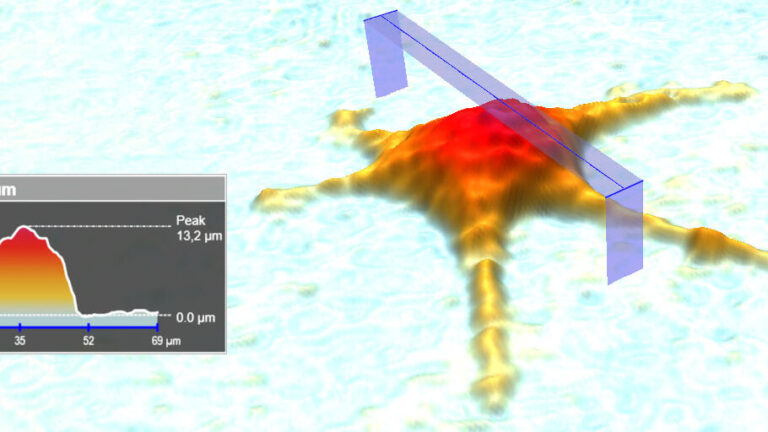
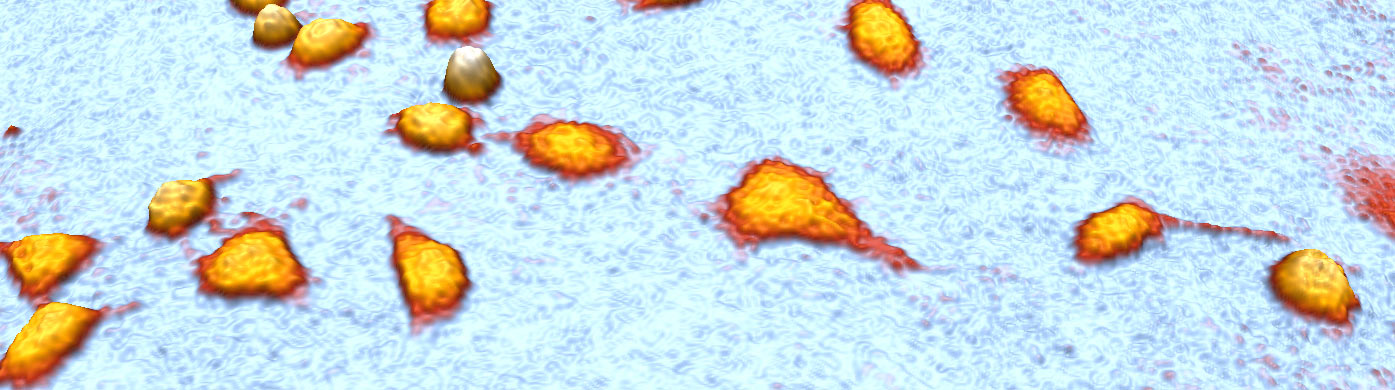
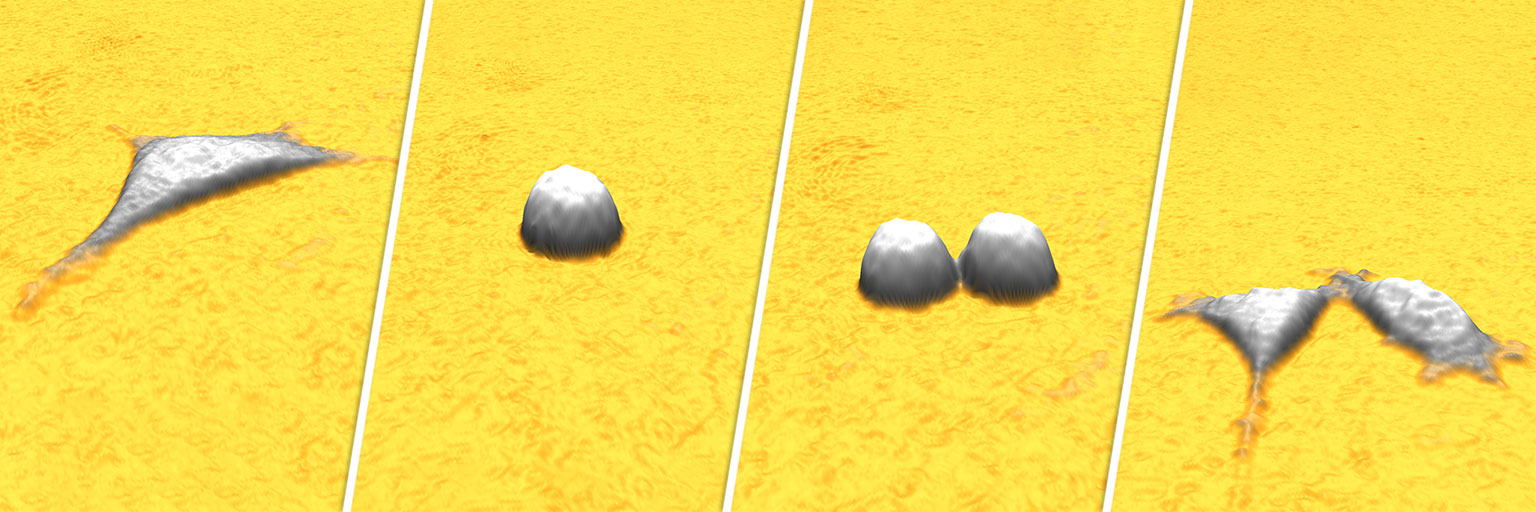
HoloMonitor uses digital holographic microscopy to collect publication-quality images without any labels. In addition, you receive accurate quantitative data. This way, you can study over 30 cell morphology parameters from a single sample and quantify cell behavior changes on both single-cell and population levels.
Bring Quantitative Imaging To Your Incubator
Label-free time-lapse video of cells proliferating over time imaged by HoloMonitor.
Publications with cell proliferation studies
Get inspired by other research fellows and learn how HoloMonitor quantitative live cell imaging can benefit your cell proliferation study
BRAFV600E induces reversible mitotic arrest in human melanocytes via microRNA-mediated suppression of AURKB
Authors: McNeal et al. Journal: eLife (2021)
In this study, to investigate why the same mutation has such different consequences in moles and melanomas, the authors using HoloMonitor studied cell proliferation, cell dry mass, cell death and cell growth rate. The experiments showed by increasing the levels of two microRNAs in melanocytes induces mitotic failure, genome duplication, and proliferation arrest. BRAFV600E induces a similar proliferation arrest in primary human melanocytes that is both reversible and conditional depending on the differentiation state of the melanocyte. Read more…
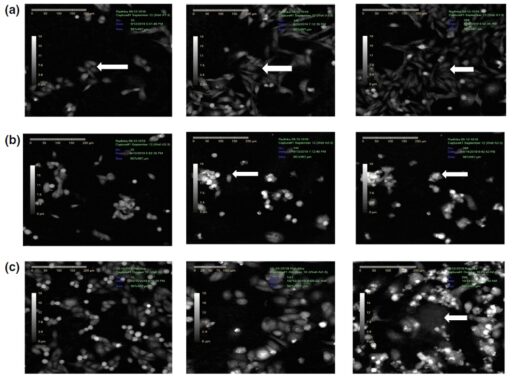
Targeted Delivery of Combination Therapeutics Using Monoclonal Antibody 2C5-Modified Immunoliposomes for Cancer Therapy
Authors: R. Narayanaswamy et al. Journal: Pharmaceutical Research (2021)
In this study, the authors have used monoclonal antibody-modified immunoliposomes for the targeted delivery of paclitaxel and salinomycin for cancer therapy. By using HoloMonitor M4, the authors measured the cell morphology, proliferation and cell division change between treatments, the results confirmed the efficacy of the antibody-targeted liposomal preparation in the therapy of cancer by giving significantly better cellular division arrest profiles and cell death. Read more…
More Featured Publications

Polysaccharide-based nano-engineered multilayers for controlled cellular adhesion in label-free biosensors
Journal: International Journal of Biological Macromolecules (2023)
Research Areas: Materials Science
Cell Lines: MC3T3-E1
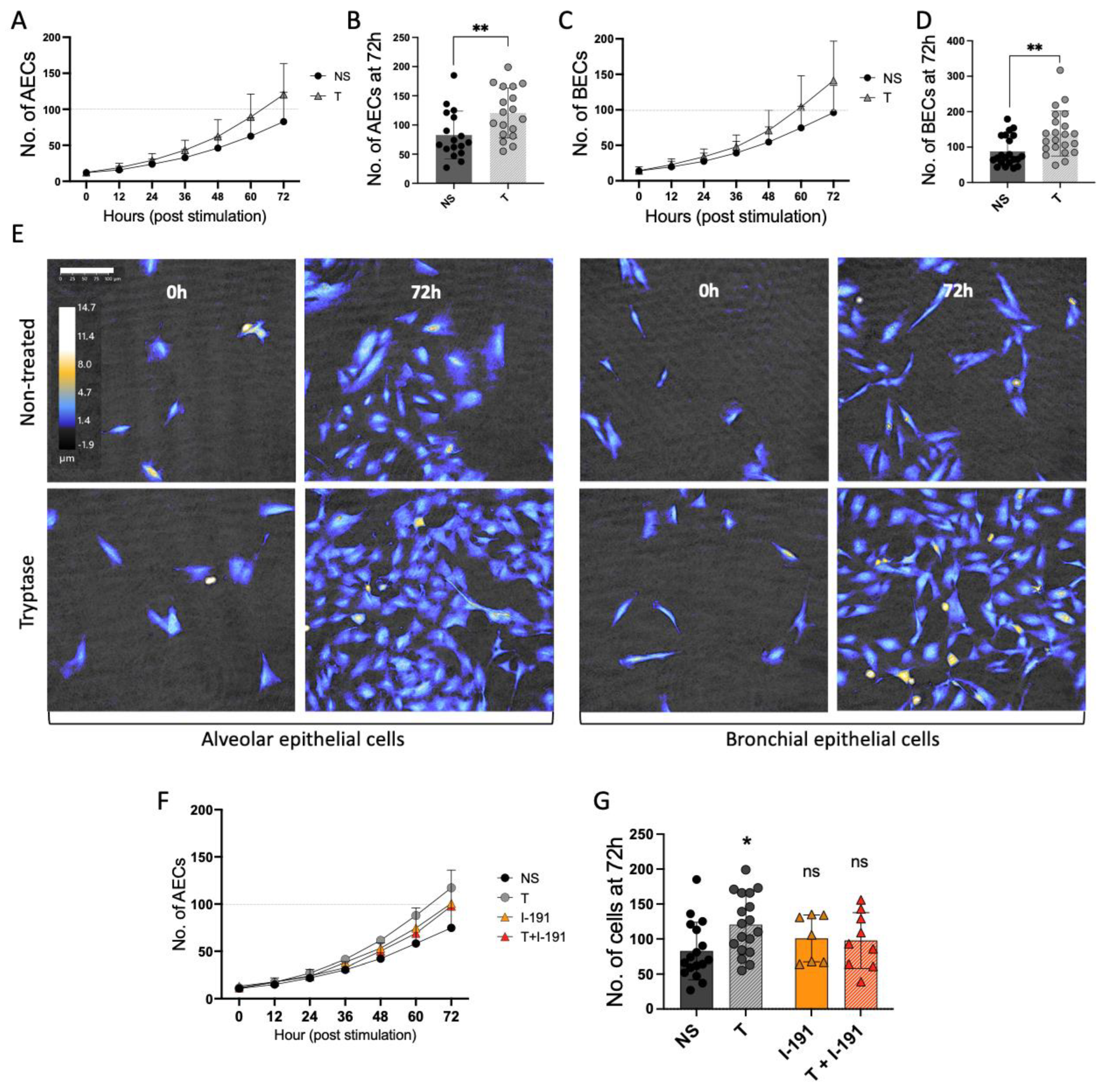
Mast Cell Tryptase Promotes Airway Remodeling by Inducing Anti-Apoptotic and Cell Growth Properties in Human Alveolar and Bronchial Epithelial Cells
Journal: Cells (2023)
Research Areas: Cell Biology
Cell Lines: BECs, BEAS-2B, AECs, A549

A role for androgen receptor variant 7 in sensitivity to therapy: Involvement of IGFBP-2 and FOXA1
Journal: Translational Oncology (2023)
Research Areas: Cancer Research
Cell Lines: LNCaP, 22Rv1, VCaP
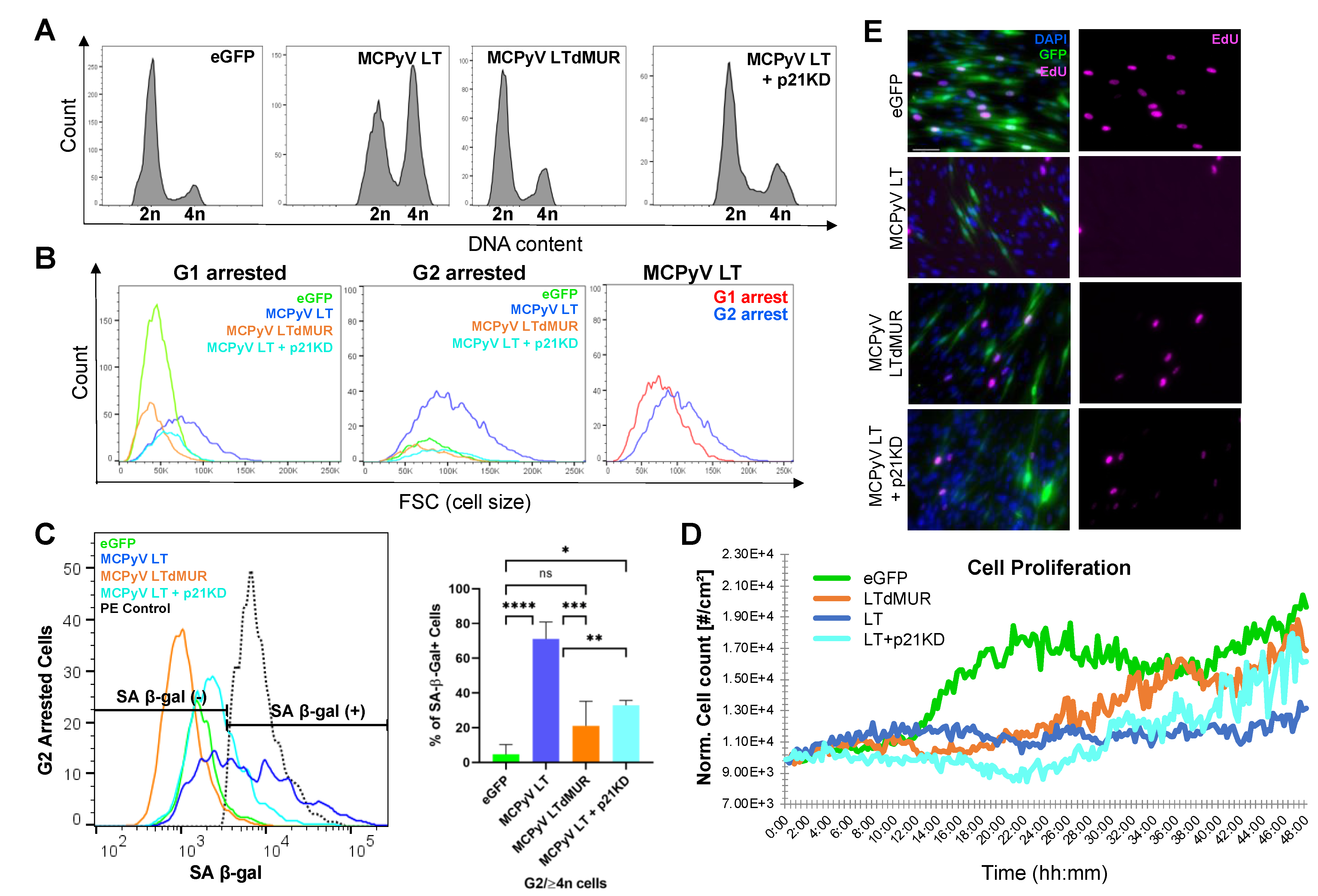
Merkel Cell Polyomavirus Large T Antigen Induces Cellular Senescence for Host Growth Arrest and Viral Genome Persistence through Its Unique Domain
Journal: Cells (2023)
Research Areas: Cancer research
Cell Lines: BJ-hTERT, 293FT, HFF-1, BJ
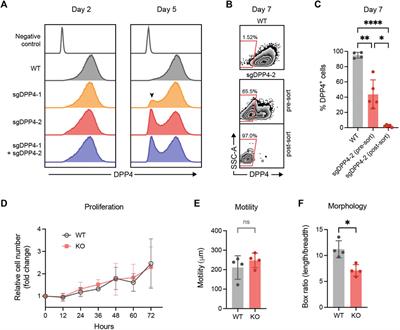
Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 expression is not associated with an activated fibroblast phenotype in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
Journal: Frontiers in Pharmacology (2022)
Research Areas: Pharmacology
Cell Lines: Primary human lung fibroblasts

Alpha-Amylase Inhibits Cell Proliferation and Glucose Uptake in Human Neuroblastoma Cell Lines
Journal: BioMed Research International (2022)
Research Areas: Cancer research
Cell Lines: SHSY5Y, LA-N-1