The Commentaries

Fighting cancer with nanoparticles
Using HoloMonitor, scientists at Northeastern University have shown that paclitaxel-resistant ovarian cancer cells stopped multiplying by cell division when treated with nanoparticles. Ovarian cancer causes more deaths than any other cancer of the female reproductive system.
Learn more …
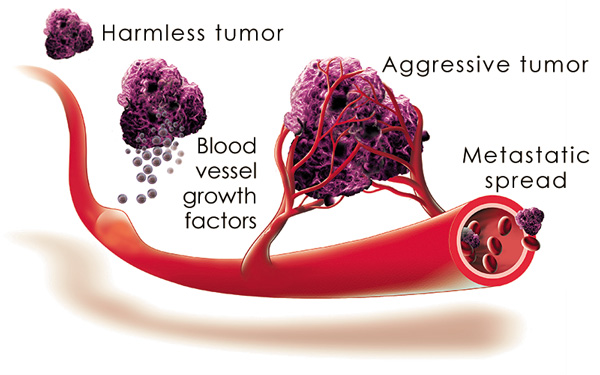
No Blood, No Tumor
Scientists at Boston Children’s Hospital have used HoloMonitor to study living bone cancer cells. By studying their dynamics, they have successfully for the first time distinguished aggressive bone cancer cells that promote blood vessel formation from the harmless counterparts that do not promote blood vessel formation.
Learn more …

Big Data, Fewer Cells
Scientists at Holographic Imaging Cytometry Program of Excellence at Northeastern University have developed a method to compare time series data of drug treated cells with untreated cells.
Learn more …
3D Culture
Using HoloMonitor and a public domain image processing software called Image J, the researchers from Northeastern University have developed a method for cell experiments based on cells cultured in a 3-dimensional collagen gel. They show that this new method is clearly superior to conventional methods, based on cells cultured on a 2-dimensional.
Learn more …

Big Pharma, Big Data
Imaged-based time-lapse cytometers, as our HoloMonitor, creates huge amounts of information on how cells interact and multiply over long time periods. Combined with Big Data technology, such novel instrumentation will provide cell biologists and the pharmaceutical industry with a game changing new tool to better understand complex cellular interactions and through this hopefully cure cancer.
Learn more …

Label-free High Content Screening
The current form of high-content screening is based on conventional microscopy. The core technology of HoloMonitor, holographic time-lapse microscopy, creates 3D-movies of unstained living cells that can be computer-processed without requiring the use of toxic labels. This new ability opens the door to more realistic high-content screening of living cells and their behavior over time.
Learn more …
