Customer Publication
Shikonin as a WT1 Inhibitor Promotes Promyeloid Leukemia Cell Differentiation
Journal: Molecules (2022)
Research Areas: Cancer research
Cell Lines: HL-60 (acute myeloid leukemia cell line)
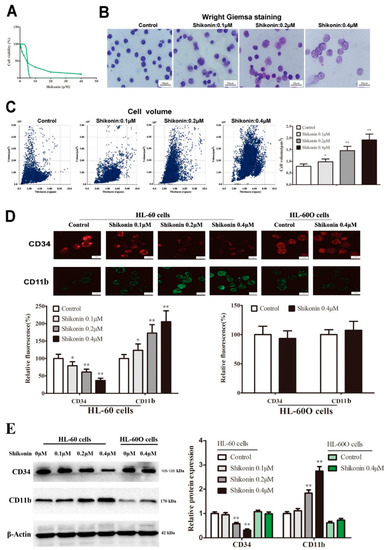
Summary: This study aims to observe the differentiating effect of shikonin on Wilms’ tumor 1 (WT1)-positive HL-60 cells and investigate the fate of the differentiated leukemia cells. WT1 overexpression unaffected cell viability but promoted resistance to H2O2-induced DNA injury and cell apoptosis. The binding of shikonin to the WT1 protein was confirmed by molecular docking and drug affinity reaction target stability (DARTS). Shikonin at the non-cytotoxic concentration could decrease the WT1 protein , simultaneously reduce the CD34 protein, and increase the CD11b protein in a dose-dependent manner in normal HL-60 cells but not in WT1-overexpressed HL-60 cells. Long-term treatment of Shikonin for HL-60 attenuated cell proliferation, prevented the cell cycle and promoted cell apoptosis. HoloMonitor M4 was used to monitor the cell morphological changes with shikonin treatment.